Establishing Thai Tax Residence: The Ultimate Guide
November 14, 2023
This article looks at ways of establishing Thai tax residence and provides information on taxes in Thailand.
Thailand is a Southeast Asian country on the Indochinese peninsula. The country is a popular travel destination, with a lot of diversity and cultural charm to share with all. But how is this country for tax residency?
If you’re considering moving overseas and aren’t sure where the best place is for you, look no further. Our team at Nomad Capitalist can help you make the best choice for you and your business.
Why Thailand?
Thailand is a relatively affordable country that appeals to entrepreneurs and business people from the West. The unique culture and fun atmosphere make it an ideal place for young people looking to escape the hustle and bustle. Thailand doesn’t offer the same opportunities as some other nations, but it has plenty to offer.

What Does Tax Residence Mean in Thailand?
Whether you incur a tax liability in Thailand depends on residence and source rules regarding taxable income.
You are considered a Thai tax resident by the tax authorities in Thailand if you are present in the country for a total of at least 180 days in a given tax year.
Previously, foreign-sourced income was only taxable if received and remitted to Thailand within the same calendar year. This has now changed.
New tax rules, which will be introduced in 2024, will mean that all foreign income will be taxed no matter when remitted, including employment, business, or sales of assets.
Thankfully, it’s not all negative, and there are still ways to structure it in a tax-efficient way. It will still be possible to transfer savings from a foreign bank account, and it should not be taxable.
The burden of showing that these are savings will fall on you.
Personal income tax must be filed by March 31. According to the Thai Revenue Code, individual taxpayers are classified into five categories, and assessable income is into eight categories.
When it comes to such income as employment income, all tax benefits are assessable unless expressly exempt by law. These include bonuses, bounties, directors’ fees, gratuities, house rent allowances, salaries, and wages.
Investment income is subject to personal income tax. That taxable income includes interest, dividends, and all other investment income.

What Is Tax Non-Residence in Thailand?
If you reside in Thailand for less than 180 days in a given tax year, you are not considered a resident of Thailand for tax purposes.
Before leaving Thailand, you would need to file the normal income tax return on income derived in Thailand. Fifteen days before you leave, apply for a Tax Clearance Certificate from the Revenue Department. This should verify that your income was non-taxable by the Thailand tax authority.

How to Obtain an Income Tax Certificate in Thailand
If you want to get your hands on a Thai tax certificate that is issued every year, you will need to fulfill these two conditions:
- Stay in Thailand for at least 180 days
- File an annual income tax return, even if you do not have taxable income derived from sources in Thailand
These certificates are an important part of safely arriving and departing from Thailand. These certificates tell the immigration agencies that you’ve fulfilled your obligations to the country.
Filing an Income Tax Return
It is possible to file a tax return even if you do not have taxable income. You can pay a tax donation to get the tax certificate in lieu of this taxable income.
If you have never filed a tax return to a tax authority in Thailand on your gross income, you should get a tax certificate with a tax ID.
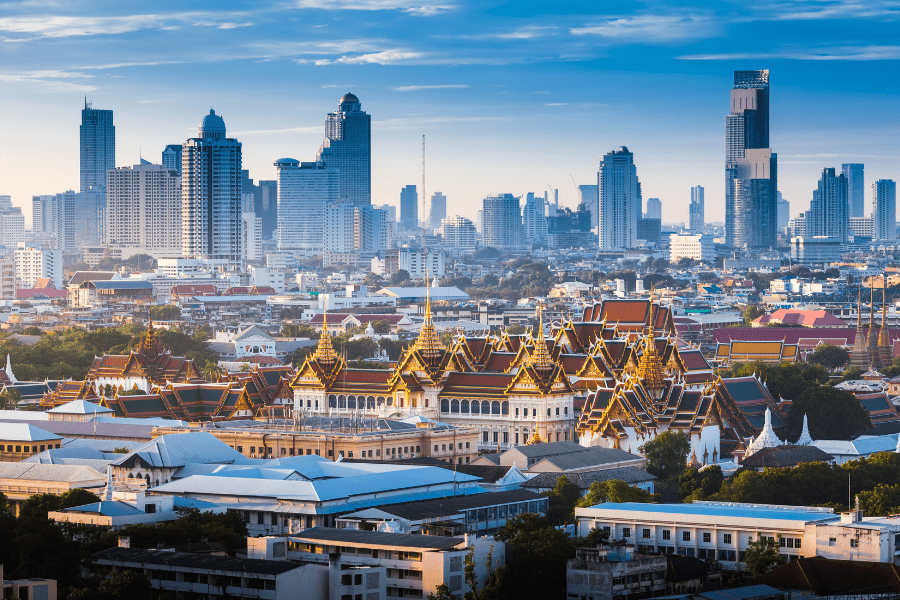

Corporate Income Tax in Thailand
A domestic corporation is subject to tax on worldwide income that is considered foreign-sourced income.
A foreign corporation pays tax on income generated in Thailand.
However, the net profits of foreign corporations carrying on business in Thailand and those of domestic corporations are taxed at the same rate. This rate on net profits benefits regional operating HQs and their employees.
VAT, specific business tax, and stamp duty are exempt from a qualifying partial business transfer from the revenue department. However, this tax exemption does not cover corporate income tax. Therefore, if your corporation makes any gains from the transfer, you may be subject to any outstanding tax.
All companies and partnerships established by Thai or foreign law that carry on business in Thailand are liable to pay corporate income tax by the revenue department.
Interest paid to a Thai company that does not fit the definition of a financial institution makes your business liable for a 1% advance withholding tax.
Foreign corporations not carrying on business in Thailand but deriving certain types of income from or in Thailand, typically via service fees, royalties, interest, dividends, capital gains, rent, or professional fees, are subject to a flat corporate income tax rate. This final tax is collected as withholding tax based on gross income.
Controlled Foreign Corporation Rules
Thailand has no tax provisions concerning controlled foreign corporations (CFCs).
Permanent Establishment Rules
A company is considered to have a permanent establishment (PE) in Thailand when it has an employee, a representative, or a go-between in Thailand for conducting business in Thailand, and if, through that representative, the company derives income or gains in Thailand. In this case, a standard corporate income tax (CIT) rate of 20% applies.
A type of PE that would need to be registered with the Ministry of Commerce is a branch office of a foreign company. The cost and the time involved in setting up a branch depend on the size and complexity of the business the branch will be carrying out in Thailand.
Other types of PE, including branch offices, may be required to apply for a foreign business permit, depending on business activities conducted in Thailand.
Under Thai law, having one employee conducting business in Thailand will be deemed to be carrying on business in Thailand for income tax purposes.
However, a foreign company is not deemed to have a PE in Thailand if the business is done through a broker, general commission agent, or any other agent of independent status.
Conclusion
Understanding the Thai Revenue Code is the key to working out the related issues of personal income tax, corporate income tax, income tax liability, and taxable income. The tax authorities in Thailand are pretty transparent when it comes to assessable income and capital gains.
Thailand can be a great choice if you’re looking for a place to settle after retirement. But it might not be the best choice for you if you’re looking to expand your business within the country.
However, thanks to its no-double tax agreement with over 60 countries, you might be able to avoid paying double taxes.
What Nomad Capitalist does is evaluate all the different options. We have helped our clients move to 31 different countries. There are a lot of pieces to the puzzle, and we look at the whole picture.
Our team at Nomad Capitalist are experts at helping our clients make the best financial and personal choices. We prioritize your goals and well-being and ensure that you go where you’re treated best.
Thailand Tax FAQ
If, as a Thai tax resident, you earn foreign-sourced income from capital gains and do not transfer the income to Thailand until the following tax year, you will not be liable to pay personal income tax on that income.
No, the value-added tax is not applied to your employment income if you are a tax resident in Thailand.
Yes, Thailand has agreed on double tax treaties with more than 61 countries. So, the withholding tax rate on dividend income received, or interest and royalties paid to a foreign entity that is a tax resident of one of the countries Thailand has a double taxation treaty with, may be reduced or exempted.
Tax credit for income tax paid abroad is granted by a Royal Decree issued under the Revenue Code and double taxation agreements. This tax treaty means that income tax paid in a foreign country can be used as a credit against Thai income tax paid. However, the amount of tax credit permitted must not exceed the Thai income tax levied on the same income.
The Thai Government is the central tax authority, and the principal tax law in the country is the Revenue Code. This enforces personal and corporate income tax, value-added tax, specific business tax, and stamp duties. The Customs Act regulates custom duties and the Excise Act excise tax.

How to Get UAE Citizenship – The Complete Guide
Sovereignty – both national and personal – shapes ambition, secures wealth, and defines status in a shifting global order. For the high-achieving global citizen, acquiring a second or even third passport is more than a lifestyle upgrade; it’s a strategic move in long-term financial and geopolitical positioning. But not all citizenships are created equal – […]
Read more

A Gateway to Central Asia: New Kazakhstan Golden Visa Program for 2025
Central Asia just raised the stakes in the golden visa game. In May 2025, Kazakhstan officially launched a 10-year Golden Visa program in an ambitious move to position the country as a serious contender in the global investor migration space. At a time when other international regions are rolling back their citizenship and residency options, […]
Read more

Top Countries Offering Golden Visas in 2025
Residency is no longer about lifestyle – it’s about leverage In an increasingly unpredictable world, Golden Visas offer something most governments can’t: certainty in exchange for capital. They are more than migration tools; they are strategic safeguards offering residence rights, future citizenship, global mobility, and access to tax-friendly jurisdictions. For investors, entrepreneurs and globally minded […]
Read more




